Navigating the Clouds: A Comprehensive Overview of Cloud Computing
History of Cloud Computing
The concept of cloud computing started in the 1950s with large mainframe computers used by government agencies and large corporations. The mainframe era laid the groundwork for shared resources and centralized computing. The term ‘cloud computing’ itself was popularized in the early 2000s, although its conceptual roots trace back to the 1960s with the development of ARPANET, which introduced the idea of virtualizing resources for broader use. By the 1990s, the internet had exploded in popularity, setting the stage for the modern cloud services we see today. The early 2000s saw the advent of Amazon Web Services (AWS), which launched in 2006, offering scalable online presence to businesses globally and introducing the model of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). This era marked significant milestones in cloud computing history, turning it into a fundamental technology that underpins the digital economy.
Defining Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is defined by the ability to provide scalable and elastic IT-related capabilities as a service using internet technologies. This model includes five essential characteristics as per the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. These features allow businesses and individuals to use computing resources like servers, storage, and applications without owning any physical hardware. The flexibility and scalability of cloud services have made them integral to modern businesses, enabling everything from data storage to complex processing tasks without the upfront cost of traditional IT infrastructure. With the cloud, users can access their resources globally through the internet, offering significant advantages in terms of mobility and collaboration.
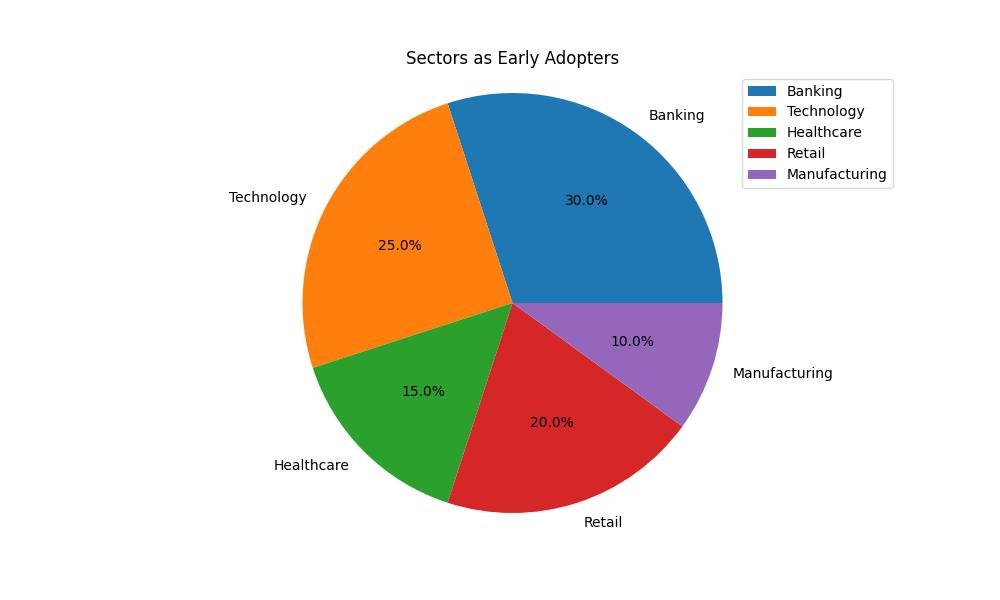
Early Use Cases and Challenges
The initial applications of cloud computing were primarily in large enterprises that could afford the early costs associated with this technology. Banks and financial institutions were among the first to adopt cloud services due to their large data management needs and the scalability cloud solutions offered. Other early use cases included Software as a Service (SaaS) applications like CRM and ERP systems, which provided businesses a cost-effective alternative to on-premises installations. However, the early days of cloud computing were not without challenges. Security concerns were paramount, with fears over data breaches and inadequate protection measures. Compliance and data sovereignty issues also posed significant hurdles, particularly for organizations in regulated industries. These challenges have shaped the evolution of cloud computing, leading to improved security measures and regulations that ensure safer deployments of cloud technologies.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages, including cost efficiency, scalability, and flexibility. Organizations can drastically reduce their IT overhead and capital expenditures by leveraging cloud-based solutions that offer pay-as-you-go pricing models. The scalability of cloud services allows businesses to adjust resources based on their current needs, providing a level of agility that is difficult to achieve with traditional IT setups. On the other hand, cloud computing also comes with its set of disadvantages. The dependency on network connectivity means that any network issues can disrupt access to critical services. Security concerns, although much improved, still pose a significant risk, especially with the increase in data breaches and cyber attacks. Privacy issues also arise as data is stored off-site, often in multiple locations, which can complicate compliance with data protection regulations. Despite these challenges, the benefits of cloud computing continue to attract more businesses, reshaping how industries operate and manage their IT resources.
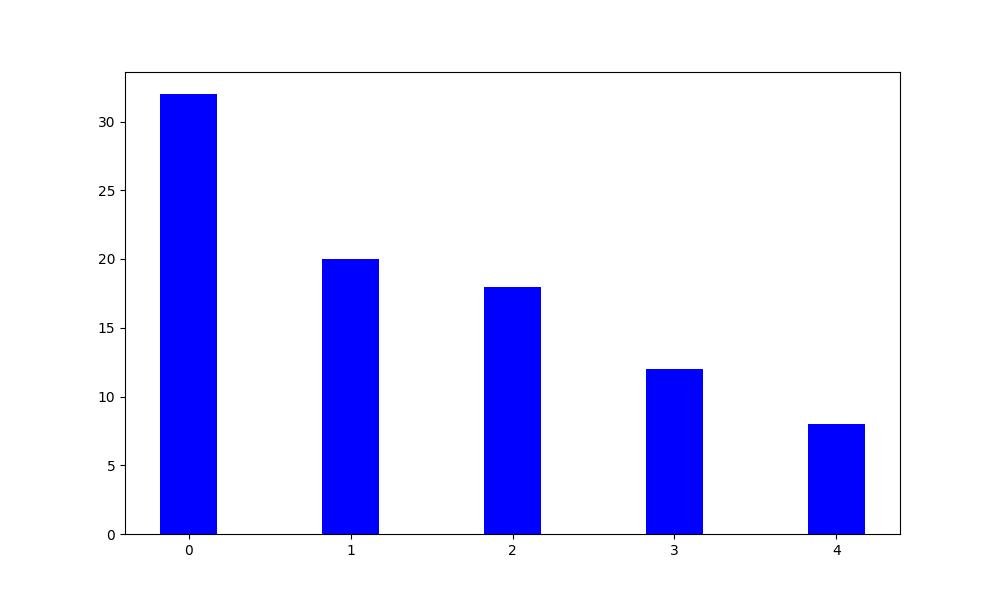
Top Cloud Service Providers and Market Share
The cloud computing market is dominated by a few major players, each offering unique platforms that cater to various business needs. Amazon Web Services (AWS) leads the pack, holding the largest share of the cloud market. Following closely are Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform, each with significant market presence. These providers offer a range of services that include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Other notable players include IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud, which also hold substantial market shares. The competition among these providers has led to innovations and price reductions, benefiting consumers. The diverse offerings allow businesses to choose the best solutions based on their specific requirements, whether they are looking for extensive computing power, innovative AI capabilities, or robust data storage options.
The Future of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing looks promising, with continuous advancements and integration into various sectors. As technology evolves, cloud services are expected to become more sophisticated, offering even greater efficiencies and capabilities. The integration of AI and machine learning into cloud platforms is anticipated to make these services more intelligent, automating complex tasks and providing deeper insights into data. The proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) is also expected to drive further growth in cloud computing, as more devices become interconnected and generate vast amounts of data. Moreover, the push towards sustainable technology solutions is likely to see cloud providers increasingly focusing on reducing their environmental impact. The future will also see a rise in hybrid and multi-cloud environments as businesses seek to optimize their operations across different platforms, ensuring flexibility and resilience in their IT strategies.
Chart6ABC